The Intellectual Capital is the knowledge resulting from resources such as ideas, inventions, technology, software programs, designs, and processes, among others, owned by the companies and which provide competitive advantage for the market. They generate value to the company, even though it is not reflected in the financial statements.
The Intellectus model will be implemented to identify the intellectual capital, which is the main objective of this project. The model was developed by the Center of Research on Knowledge Society (CIC by its acronym in Spanish) of Universidad Autónoma de Madrid and it was designed to identify and manage intangible or knowledge values that make up the concept of enterprises Intellectual Capital. The following chart illustrates the model:
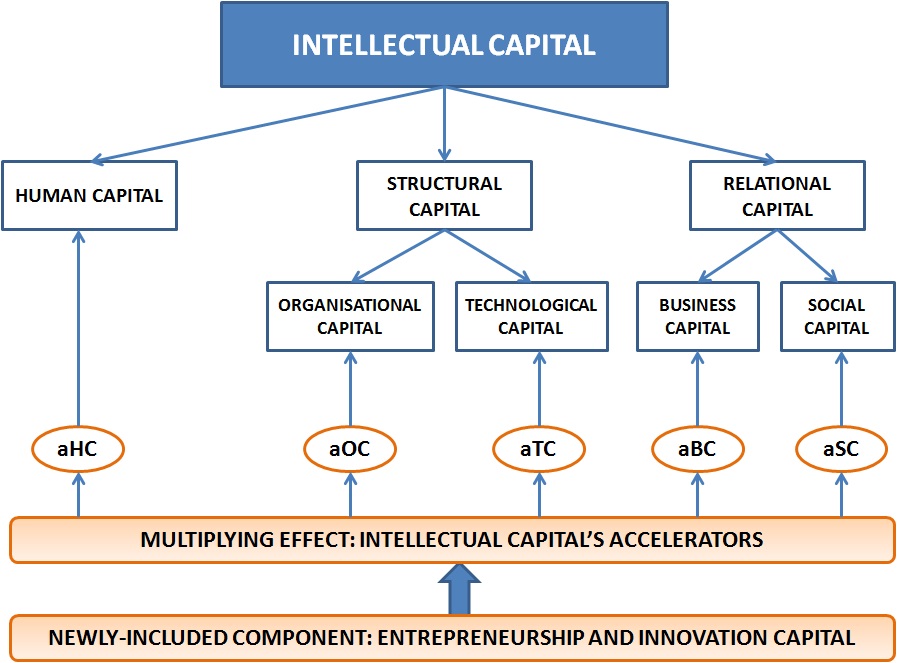
HUMAN CAPITAL
Human capital refers to the explicit or tacit, individual or social knowledge people and groups of people have as well as their capacity to create it and which is useful for the organization's strategic purpose. Human capital is made up of what people and groups of people know and their capacity to learn and share such knowledge with others, so that once it is codified, it can benefit the organization.
STRUCTURAL CAPITAL
The Structural Capital is the body of knowledge and intangible assets derived from the action processes owned by the organization and which will remain after people leave. It is composed of the Organizational Capital and Technological Capital.
Organisational Capital
The Organizational Capital is the set of explicit and implicit intangible assets explicit and implicit in nature, both formal and informal that effectively and efficiently structure and develop the organization's identity and activity.
Technological Capital
The Technological Capital refers to the set of intangibles directly related to the development of activities and functions of the organization’s technical system. They are responsible for both the creation of the product itself (goods and services), and the progress in the base of the knowledge needed to develop future innovative products and processes.
RELATIONAL CAPITALThe Relational Capital is the set of knowledge that is incorporated in the organization and its people as a result of the value derived from the number and quality of the relations they continuously establish with different market agents and with society at large. Business Capital and Social Capital make up the Relational Capital.
Bussiness Capital
Business Capital refers to the value that the relations, which are kept with the main agents linked to its basic business process, represent for the organization.
Social Capital
Social Capital refers to the value that the relations that are kept with the remaining social agents operating in its social and territorial environment represent for the organization. It is expressed in terms of integration, commitment, cooperation, cohesion, connection and social responsibility the organization wants to establish with society.
Methodology In order to achieve the objectives, this project aims at the development of a case-study methodology based on the development of the following stages:
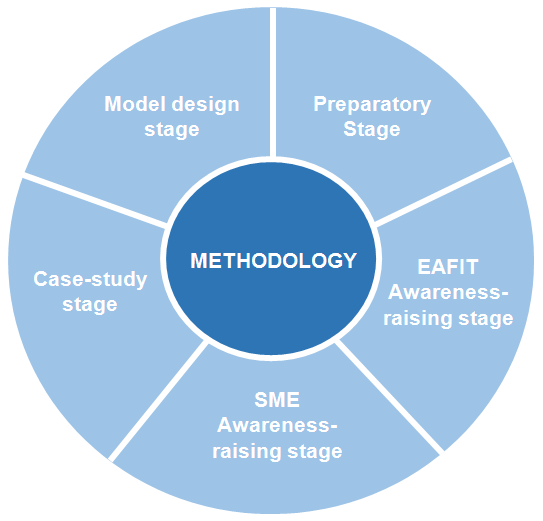
- Preparatory stage: aimed at establishing an initial contact and adjusting the project to the national reality.
- Awareness-raising stage: it is intended to develop a culture oriented towards the intellectual capital and its management as the driving force for development. This awareness raising takes place both at the institutional and corporate level.
- Case-study stage: preparation of Intellectual capital reports is suggested to a group of 15 SMEs of Antioquia.
- Model design stage: an analysis model for the development of the organization dynamic capacities will be established based on the results obtained with the companies.
CASE STUDY METHOD
The case study method is a scientific methodological research, qualitative in nature and a useful strategy to be implemented in topics virtually viewed as innovative since it studies a contemporary phenomenon in its real environment. It may be implemented for the study of a single or multiple cases.
This method allows for deeper research and broader understanding of the topic under study, thus achieving the entire research objective and allowing the analysis of different cases with different aims. (Martínez, 2006).
SAMPLE POPULATION 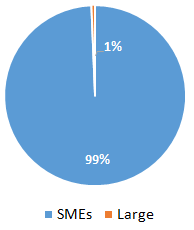
Because of their economic and social impact, SMEs are the population under study due to their contribution capacity to the GDP and employment generation. In Antioquia (study region) 99 percent of the companies are SMEs, 73 percent of them are located in Vallé de Aburrá (Medellin Chamber of Commerce for Antioquia, 2011). This is the reason why the companies selected for this project must be located in this area.
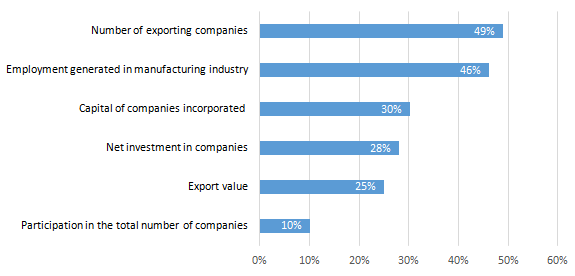
The participation of the SMEs' in Antioquia´s market in terms of exports, employment generation and exported value, among others, supports the assertion that the SMEs play an increasingly important role in the market of Antioquia and it is growing even wider (Medellin Chamber of Commerce for Antioquia, 2015).
COMPANIES' PROFILE
For the implementation of this methodology, 15 legally created, Antioquia's SMEs (ideally located in Valle de Aburrá), with a maximum of 200 employees, will be selected. These companies should be knowledge generators, with an interest in research and innovation from the implementation of new processes or products in which the execution of Research, Development and Innovation (I+D+i by its acronym in Spanish) activities is evident. In addition, Interest in participating in programs for the organization strengthening in favor of its own growth should be shown.